The macula is the center of the retina. It is a very fragile arrangement of nerves.
The macula is prone to breaking down in older age, in a common condition known as age related macular degeneration, or AMD.
AMD generally involves protein clumps called drusen forming under the macula, and death (or “atrophy”) of the macula nerve cells themselves. This is called “dry AMD.”
Patients with dry AMD usually notice blurry vision to varying degrees.
A more severe form of macular degeneration involves new blood vessels and scar tissue growing under the macula. This growth is called “wet macular degeneration” and is destructive, causing severe visual loss.

Healthy macula
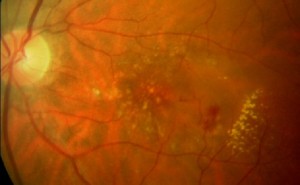
Wet AMD showing drusen blood leaking from new blood vessels under the macula.
Dry AMD may be slowed down a bit using specific therapy. Wet AMD can be treated by injecting drugs that stop new blood vessels from growing.
The National Eye Institute is an excellent resource for information on AMD.
